Introduction
The construction and engineering industry faces unprecedented challenges in establishing temporary and semi-permanent worker accommodations across remote, challenging environments—from mining operations in sub-Saharan Africa to oil and gas facilities in the Middle East, infrastructure projects across Latin America, and peacekeeping operations worldwide. Traditional construction methods for barracks prove inadequate: they consume excessive time, generate substantial on-site pollution, demand continuous skilled labor, and create inflexible spaces that fail to adapt to changing project requirements.
Modern barracks construction has undergone a fundamental transformation through the adoption of modular, prefabricated housing systems. These integrated solutions fundamentally reshape how organizations address accommodation challenges. Unlike conventional building approaches that require weeks or months of on-site construction, modular barracks arrive factory-complete and ready for immediate deployment. This evolution represents far more than incremental improvement—it constitutes a paradigm shift in how industries approach temporary and semi-permanent infrastructure.

Understanding Engineering Camps and Barracks Infrastructure
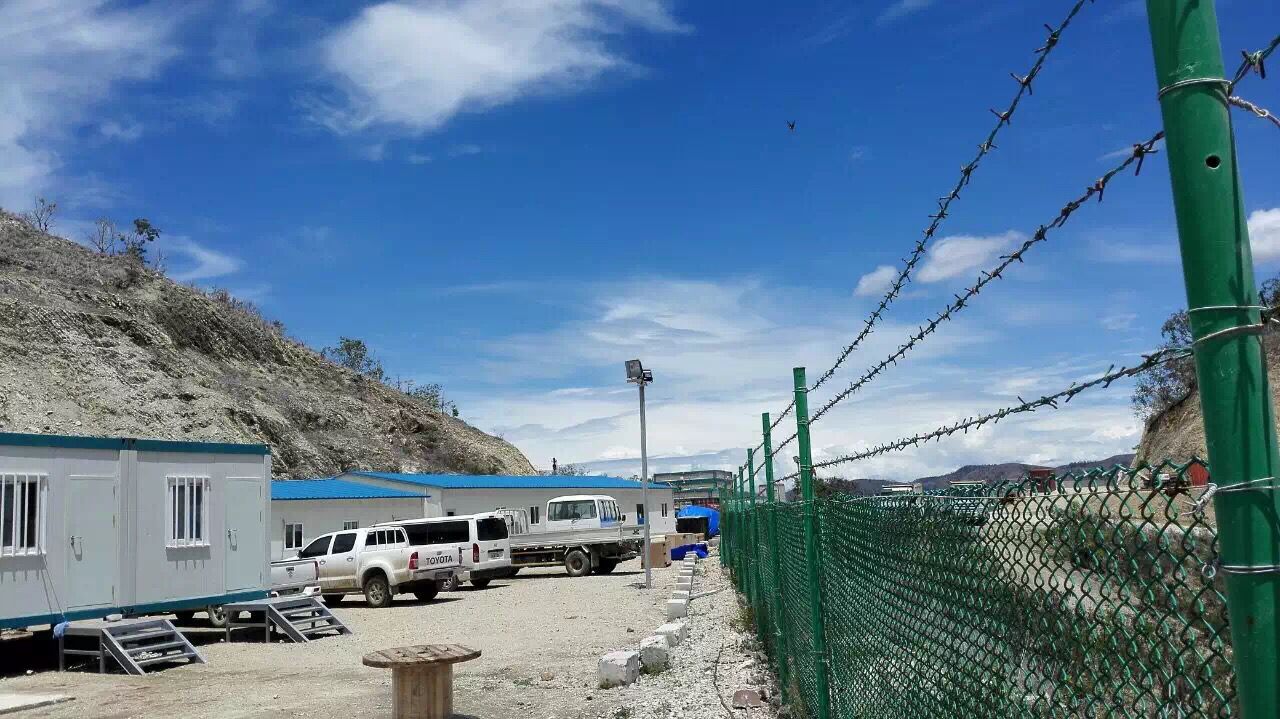
Engineering camps function as self-contained communities designed to support specific construction, mining, energy, or infrastructure projects. These installations typically operate for months to years, requiring comprehensive facilities that extend far beyond simple sleeping quarters.
A properly configured engineering camp comprises several integrated components. Accommodation facilities house workers in safe, comfortable environments equipped with basic furnishings—beds, desks, chairs, and often individual or shared bathroom facilities. Office spaces support administrative functions, project management, and documentation. Storage and warehouse facilities protect equipment and materials from environmental damage. Catering services sustain worker nutrition and morale through dedicated kitchen and dining facilities. Beyond these essentials, recreational spaces—basketball courts, gymnasiums, libraries, entertainment areas—address the psychological and physical wellness needs of isolated workforces.
The strategic advantage of purpose-designed barracks lies in workforce productivity enhancement. Workers resting in comfortable, quiet environments with adequate privacy demonstrate measurably improved performance, reduced illness rates, and enhanced retention. This productivity multiplication easily justifies investments in quality accommodation.
Traditional Barracks Construction: Limitations and Challenges
Conventional on-site barracks construction presents persistent obstacles that directly impact project economics and timelines:
Extended Construction Timelines: Traditional approaches require extensive on-site labor, multiple construction phases, and sequential task completion. Projects often face weeks or months of delays before worker accommodation becomes available.
Environmental Degradation: Large-scale earthmoving, material stockpiling, waste generation, and concrete pouring create substantial environmental footprints in fragile ecosystems—particularly problematic in ecologically sensitive regions.
Cost Inefficiency: Repeated site-specific design, material sourcing, skilled labor recruitment, and logistics coordination across diverse geographic locations eliminate economies of scale and inflate project expenses.
Inflexibility: Once constructed, traditional barracks resist modification. Changing project scope, workforce size adjustments, or facility repurposing requires costly demolition and reconstruction.
Quality Consistency Issues: Different construction teams, varying local standards, and environmental factors create unpredictable results. Quality fluctuates significantly across projects.
Revolutionary Modular Barracks Solutions
Modern modular housing systems address each traditional limitation through factory-controlled production and design standardization.
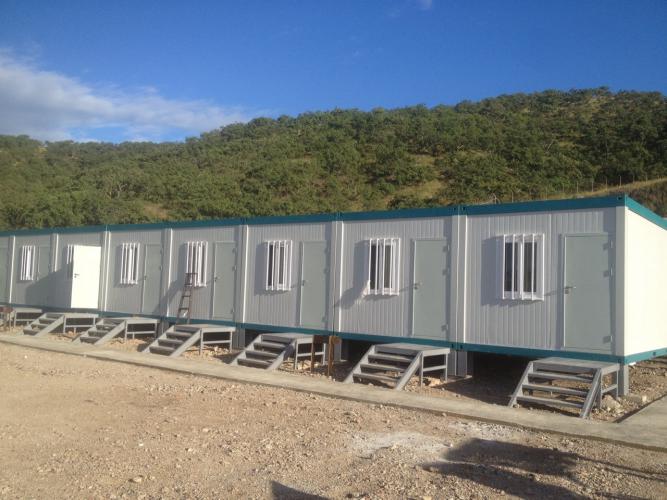
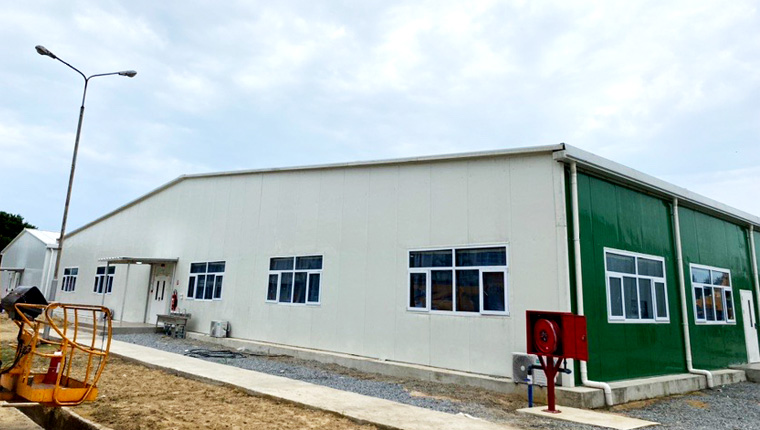
Container Houses: Standardized Modularity
Container houses represent the foundation of contemporary barracks construction. These units adopt standardized dimensions—typically 6,055mm in length (5,845mm interior), 2,990mm in width (2,780mm interior), and 2,896mm in height (2,500mm interior)—enabling unlimited horizontal and vertical combinations. A single container can function independently as a dormitory, office, or storage unit. Multiple containers stack vertically up to three levels or arrange horizontally to create expanded dormitory blocks, office complexes, or specialized facilities.
Technical Specifications:
| Specification | Value |
| Unit Weight (Empty) | 1,520 kg |
| Steel Frame Material | Hot-dip galvanized Q235 steel |
| Roof Insulation | 100mm glass fiber wool |
| Floor Insulation | 100mm glass fiber wool |
| Wall Insulation | 75-100mm rock wool or glass wool |
| Roof Live Load Rating | 0.5 KN/m² |
| Floor Live Load Rating | 2.0 KN/m² |
| Wind Load Rating | 0.5 KN/m² |
| Service Life | 10-15 years (mobile) |
The modular design principle transforms manufacturing efficiency. Container production becomes standardized, repetitive, and mechanizable—dramatically reducing unit costs while improving consistency. Factory prefabrication of all components—electrical systems, water supply, drainage, interior finishes—eliminates on-site secondary decoration. Units arrive turnkey, requiring only connection and deployment.
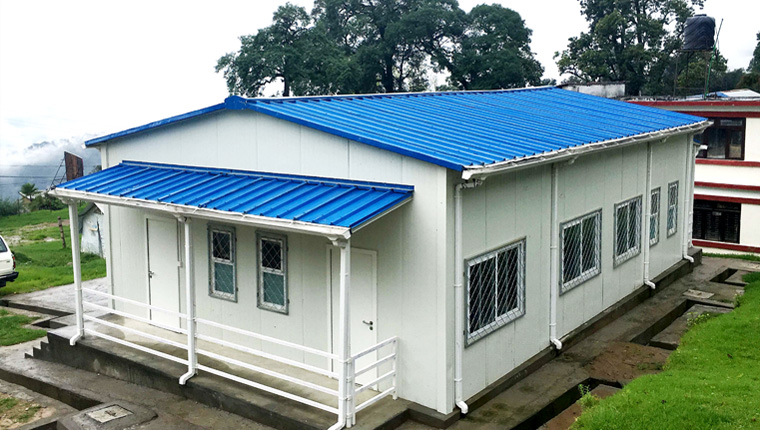
ZA-Type Integrated Houses: Flexible Semi-Permanent Solutions
ZA-type houses represent an evolution beyond basic container housing, offering customizable design while maintaining rapid deployment advantages. These structures employ cold-formed, hot-dip galvanized steel frameworks, enabling both standardized configurations and personalized designs tailored to specific customer requirements.
Distinctive Advantages:
Structural Resilience: Withstands Category 11 winds; withstands Category 17 hurricanes with special treatment
Corrosion Resistance: Thin-walled hot-dip galvanized construction provides superior corrosion protection compared to spray-painted alternatives
Accelerated Production: Mechanized mass production achieves dramatically shortened processing cycles
Exceptional Sealing: Structural frames positioned internally with external maintenance plates create seamless connections
Rapid Installation: Fully bolted connections eliminate on-site welding, substantially reducing construction duration
Design Flexibility: Personalized customization based on customer specifications and functional requirements
ZA-type houses have proven effective across diverse applications—from dormitories and offices to restaurants, recreation facilities, and specialized functional spaces. Geographic deployment ranges span extreme temperature environments (from arctic cold to desert heat), coastal regions requiring enhanced corrosion resistance, and high-altitude locations.
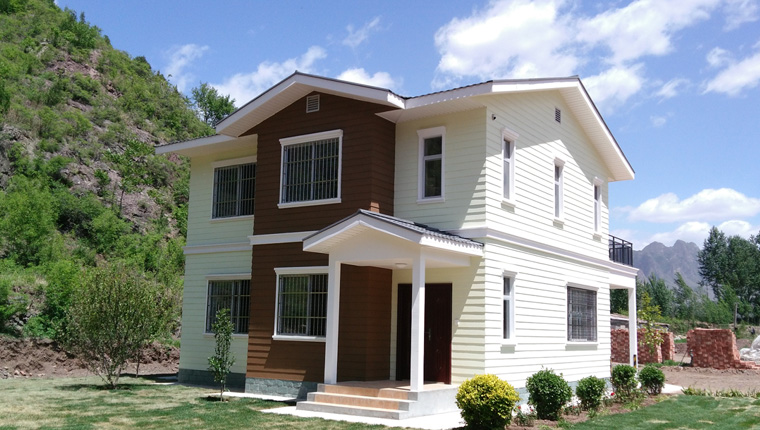
Light Steel Villas: Premium Semi-Permanent Housing
For extended-duration projects requiring superior comfort and aesthetics, light steel villas offer semi-permanent solutions with design life exceeding 25 years. These structures employ sophisticated modular systems with through-column structural design, improving stress distribution and enabling greater architectural flexibility.
Distinctive Characteristics:
Service Life: Designed for 25+ year operational duration
Customizable Design: Layout and decoration adapt to individual user requirements and climate-specific considerations
Rapid Construction: Modular assembly dramatically reduces build timelines compared to traditional construction
Environmental Responsibility: Substantially reduces on-site construction pollution and material waste
High-End Aesthetics: Appearance and functionality approach permanent residential standards
Light steel villas function optimally for projects where workforce stability, extended worker tenures, and operational longevity justify premium housing investments. They effectively transition from temporary project accommodation to permanent operational facilities as projects conclude their active construction phases.
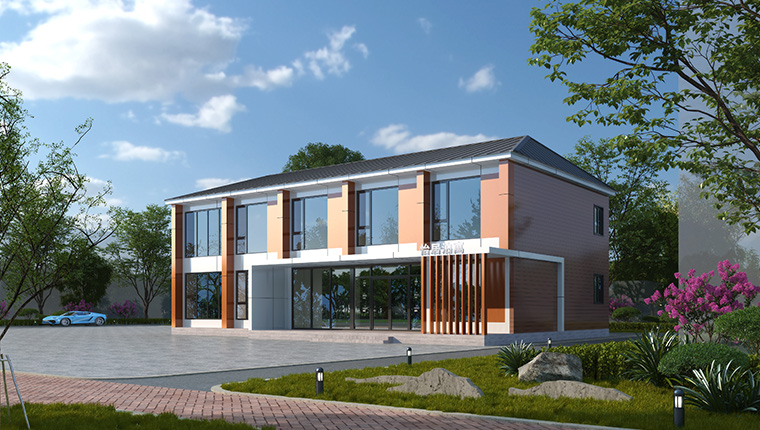
Light Steel Modular Products: Integrated Wall Systems
Advanced light steel module products employ sheet-type modular systems with through-column structural design, optimizing structural stress performance. Integrated modular walls incorporate both structural and enclosure functions, facilitating rapid assembly.
These systems offer manufacturing flexibility: complete factory prefabrication for immediate hoisting installation, or semi-prefabricated configurations requiring on-site assembly. Advantages include modular design efficiency, earthquake resistance, wind resistance, fire protection capabilities, thermal insulation, and abbreviated construction periods. Primary applications span apartment buildings, hotels, commercial facilities, and office complexes.
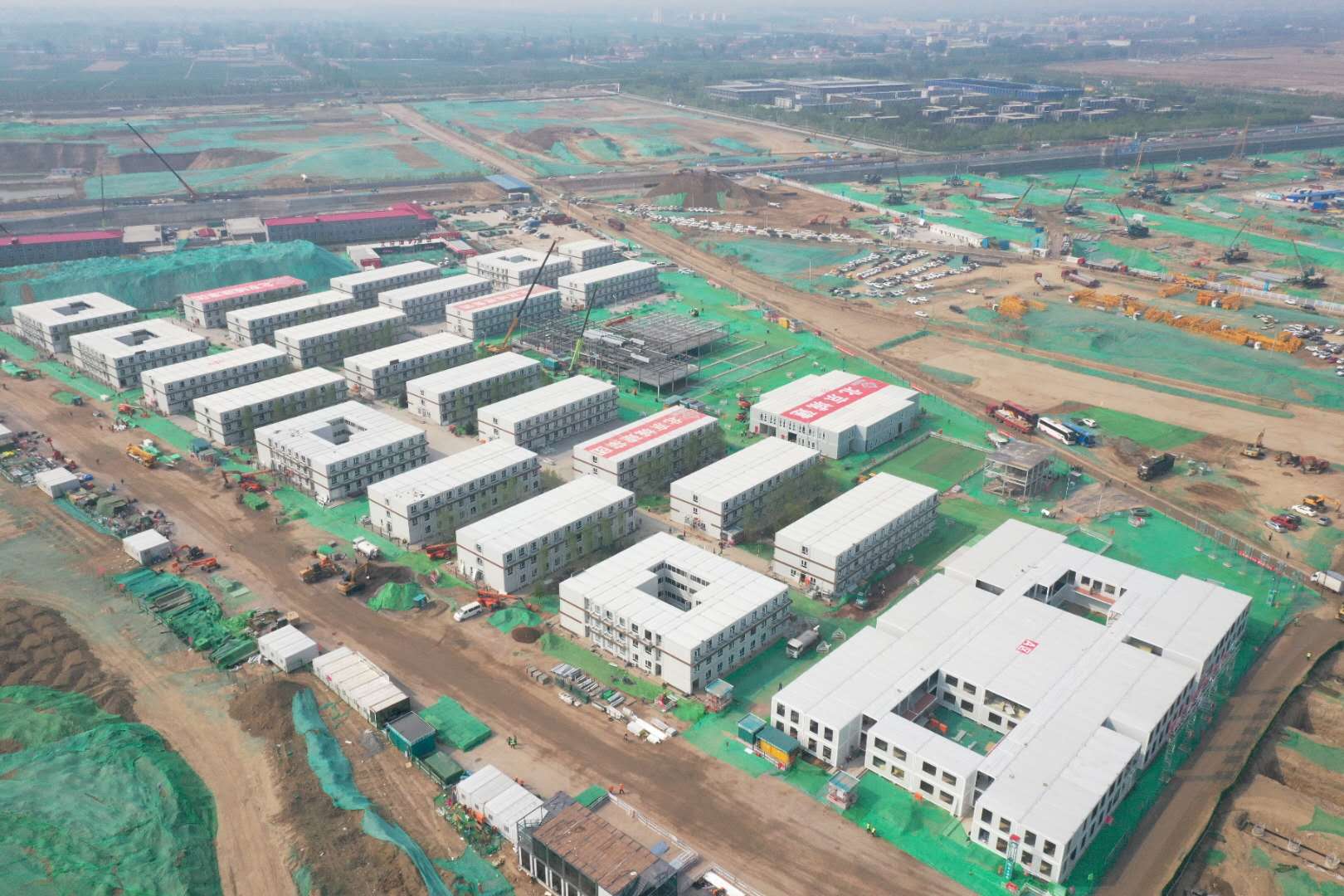
Production Capabilities and Global Reach
Modern barracks manufacturers maintain substantial production infrastructure supporting global deployment. A leading modular housing provider operates container house manufacturing facilities with annual production capacity exceeding 40,000 units, distributed across multiple regional production centers positioned strategically across Africa, Asia, Europe, and the Americas.
The company has successfully completed projects across more than 100 countries, establishing comprehensive logistical networks ensuring reliable transportation, site installation, and after-sales service. This global footprint enables rapid response to emerging project requirements while maintaining consistent quality standards across diverse geographic and climatic conditions.
Key Applications and Project Examples
Modern barracks systems demonstrate exceptional versatility across numerous industrial and infrastructure sectors:
Mining and Energy Operations
Remote mining and oil/gas facilities frequently require accommodation for hundreds or thousands of workers in locations lacking established infrastructure. Modular barracks solve critical challenges:
Rapid Deployment: Critical operational phases begin quickly; production efficiency maximizes from project inception
Workforce Stability: Quality accommodation reduces turnover, stabilizes experienced teams, and improves operational safety
Environmental Protection: Controlled, contained facilities minimize ecological impact in sensitive regions
Economic Efficiency: Reduced on-site construction requirements lower project overhead
Notable deployments include major refinery projects, mineral extraction operations, and hydrocarbon exploration facilities where workforce accommodation directly impacts project success.
Infrastructure and Transportation Projects
Major railway, highway, and airport projects require substantial worker accommodation for extended periods. Recent examples include:
Airport Expansion Projects: Maldives Velana International Airport utilized double-layer ZA and ZM barracks covering 15,600 square meters, comprising office buildings, staff dormitories, medical facilities, and support spaces
Railway Construction: Extensive railway electrification and expansion projects across Africa and Asia employ modular housing accommodating thousands of construction workers
Educational and Commercial Facilities
Educational institutions and commercial enterprises increasingly leverage modular construction:
School Expansion: Enhanced sound insulation, indoor lighting, and safe material selection protect student populations while maintaining rapid project timelines
Hospitality: Hotel and resort projects benefit from customizable design flexibility, allowing unique aesthetic expressions while maintaining deployment speed advantages
Disaster Relief: Integrated housing systems provide rapid humanitarian response capacity, establishing functional communities within days rather than months
Critical Design Considerations for Barracks Construction
Successful barracks planning requires attention to multiple environmental and functional variables:
Climate Adaptation
Barracks design must account for specific climatic conditions where deployment occurs. Desert environments demand specialized air conditioning systems and heat reflective materials. Arctic deployments require enhanced insulation, heated infrastructure, and weatherproofing. Coastal locations necessitate corrosion-resistant materials and protective coatings. Tropical regions require moisture management and ventilation optimization.
Structural Engineering
Modular barracks must accommodate extreme environmental forces—hurricane-force winds, heavy snow loads, seismic activity—without compromising occupant safety. Hot-dip galvanized steel frameworks provide superior environmental resilience compared to conventional alternatives. Engineering specifications must reflect specific geographic hazards and load conditions.
Functional Layout
Barracks layout efficiency directly impacts workforce satisfaction, security, and operational effectiveness. Thoughtful design segregates accommodation, office, catering, and recreational spaces while maintaining convenient connectivity. Security considerations determine perimeter design, access control, and monitoring infrastructure. Cultural and regulatory requirements shape facility programming—separate facilities for different workforce categories, prayer spaces, gender-specific accommodations.
Sustainability Considerations
Modern projects increasingly demand environmental responsibility. Modular construction dramatically reduces on-site waste compared to traditional methods. Reusable components eliminate single-use material extraction. Prefabrication in controlled environments reduces energy consumption and environmental pollution. Integrated waste management systems protect surrounding ecosystems.
Economic Analysis: Cost Advantages of Modular Barracks
The financial case for modular barracks solutions proves compelling across multiple dimensions:
Capital Cost Reduction: Factory mass production achieves substantial unit cost advantages compared to site-specific construction. Standardized components leverage economies of scale impossible in dispersed, single-project construction.
Timeline Compression: Reduced on-site construction duration accelerates project operational phases. Earlier project revenue generation justifies accommodation investments through reduced financing costs and accelerated returns.
Operational Efficiency: Quality accommodation reduces workforce turnover, illness-related absences, and accident rates. These productivity improvements compound across project timelines, often exceeding accommodation investment costs.
Reusability Economics: Container houses and modular structures support multiple deployment cycles across sequential projects. Unlike single-use construction, modular systems generate value across multiple project generations, distributing capital costs across extended timeframes.
Risk Mitigation: Standardized, factory-tested components reduce construction defects and performance variability. Comprehensive warranties and after-sales support address emerging issues rapidly, preventing costly operational disruptions.
Selection Criteria: Choosing Appropriate Barracks Solutions
Different project requirements demand different solution approaches. Strategic selection requires analyzing multiple variables:
Project Duration and Permanence: Short-term projects (under 12 months) favor cost-minimized container houses. Medium-term projects (1-3 years) benefit from ZA-type flexibility. Extended projects (3+ years) justify light steel villa investments offering superior longevity and comfort.
Workforce Size and Composition: Small crews may utilize individual containers; large operations require integrated complexes with diverse facility types. Workforce composition—all male vs. mixed gender, technical specialists vs. general labor—influences accommodation design and facility programming.
Environmental Conditions: Extreme climates demand specialized materials and engineering. Desert operations, arctic deployments, coastal facilities, and high-altitude locations each necessitate climate-specific design considerations and enhanced protection specifications.
Geographic Location: Remote, landlocked locations may favor locally manufactured solutions reducing transportation challenges. Coastal access enables efficient shipping of fully-prefabricated units. Infrastructure availability influences facility self-sufficiency requirements.
Scalability Requirements: Projects facing uncertain workforce dynamics benefit from modular systems supporting phased expansion or contraction. Fixed designs provide lower per-unit costs but sacrifice flexibility.
Installation and Logistics: From Factory to Site
Modern barracks deployment follows systematically refined processes ensuring reliable, efficient site establishment:
Manufacturing and Quality Control: Factory production incorporates comprehensive quality assurance protocols—structural testing, safety inspections, electrical verification, water system pressure testing. Products undergo rigorous evaluation before shipment authorization.
Transportation Logistics: Modular units package efficiently into standard shipping containers, optimizing ocean freight economics. Land transportation networks position equipment near deployment sites, minimizing final-mile logistics costs.
Site Preparation: Foundation requirements vary by configuration. Container houses typically require concrete plinths or ground-level support structures. ZA-type and light steel structures may employ concrete foundations or driven pilings depending on soil conditions and load requirements.
Installation Procedures: Professional installation teams coordinate foundation preparation, unit positioning, mechanical connections, utility integration, and final inspections. Modern procedures complete complex barracks installations within days or weeks rather than months.
Utility Integration: Water supply, electrical systems, drainage, and sewage connections integrate according to site-specific infrastructure. Backup power generation, water storage, and waste treatment systems ensure self-sufficient operation in remote locations.
Global Barracks Projects: Real-World Applications
Industry leaders have successfully deployed modular barracks solutions across diverse, challenging environments:
Nigeria Dangote Oil Refinery: Extensive barracks complex utilizing ZM steel structures and container houses, accommodating thousands of construction workers across multiple project phases.
Maldives Airport Expansion: Double-layer ZA and ZM barracks providing comprehensive accommodation, office, medical, and support facilities within strict environmental protection constraints.
Venezuela Central Power Plant: Semi-permanent light steel residential facilities designed for 25+ year operational life, addressing extended project timelines and high corrosion environments.
Iraq Saharan Power Station: Diversified barracks utilizing light steel villas, container houses, and specialized structures adapted to desert climate extremes, including custom air conditioning systems for energy efficiency.
Kenya Railway Projects: Extensive modular accommodation supporting major railway electrification initiatives across challenging geographic conditions.
These deployments demonstrate consistent excellence, reliability, and customer satisfaction across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Asia, establishing modular barracks as the industry standard for modern project accommodation.
Future Trends in Barracks Construction
Emerging technologies and evolving industry requirements continue reshaping barracks design and implementation:
Sustainability Integration: Renewable energy systems, water recycling, waste management technologies, and green building materials increasingly integrate into barracks design, addressing environmental compliance and operational cost reduction.
Smart Building Systems: IoT sensors, automated climate control, energy monitoring, and integrated security systems enhance operational efficiency while improving occupant experience and safety.
Modular Technology Advancement: Continued refinement of connection systems, weatherproofing technologies, and structural materials increases design flexibility while reducing costs and deployment timelines.
Customization Capabilities: Advanced manufacturing technologies enable greater personalization and configuration flexibility, allowing tailored solutions addressing specific project requirements while maintaining production efficiency.
Workforce Experience Enhancement: Growing recognition of workforce welfare's importance drives barracks design prioritizing occupant comfort, mental health support, communication capabilities, and recreational facilities.
Conclusion
Building barracks has fundamentally transformed through adoption of modular, prefabricated housing solutions. These integrated systems address persistent limitations of traditional construction—extended timelines, environmental impact, inflexibility, inconsistent quality—through factory-controlled production, standardized design, and rapid deployment methodology.
Container houses, ZA-type structures, light steel villas, and integrated modular products provide comprehensive solutions addressing diverse project requirements across varied climates, geographic locations, and workforce compositions. Global production capacity, refined logistics networks, and decades of accumulated deployment experience ensure reliable, cost-effective accommodation solutions regardless of project complexity or location.
Modern barracks construction directly impacts project success through accelerated operational commencement, enhanced workforce stability and productivity, and substantially reduced environmental footprints. As industries increasingly recognize workforce accommodation's strategic importance to project economics and social responsibility, modular barracks solutions represent the technological frontier of temporary and semi-permanent infrastructure.
For organizations planning major projects in remote locations, challenging climates, or extended timelines, consulting experienced modular housing providers ensures access to proven solutions, global expertise, and professional implementation support. The evolution from traditional construction to modern modular systems continues delivering measurable advantages—time compression, cost reduction, quality assurance, and operational efficiency—that define contemporary project success.
For comprehensive information about modular barracks solutions, engineering camp design, and custom accommodation requirements, visit https://www.cdph.net/



More

More

More

More

More
Learn More

























![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





